November 6, 2017
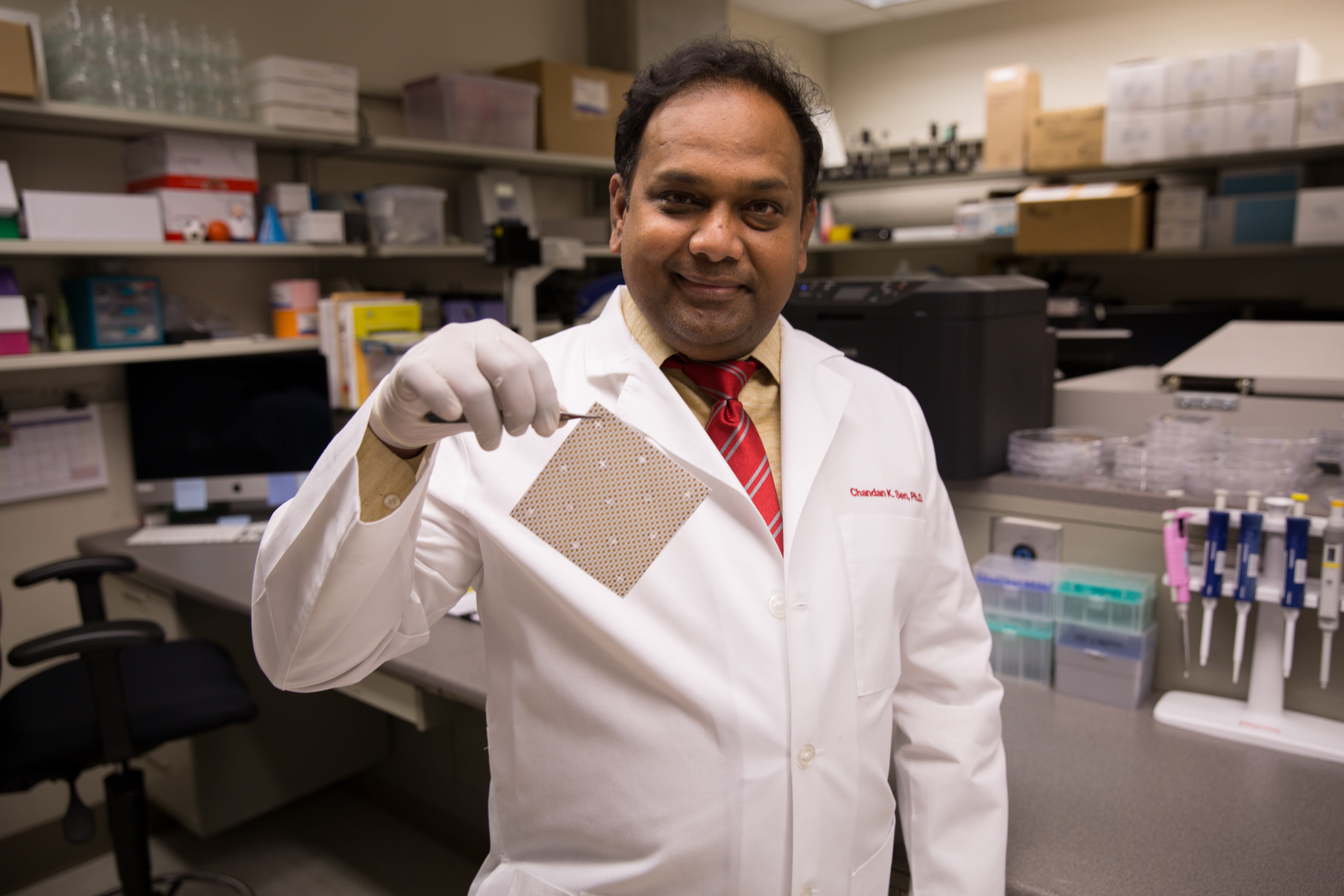 COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center have shown – for the first time – that special bandages using weak electric fields to disrupt bacterial biofilm infection can prevent infections, combat antibiotic resistance and enable healing in infected burn wounds. The dressing becomes electrically active upon contact with bodily fluids.
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center have shown – for the first time – that special bandages using weak electric fields to disrupt bacterial biofilm infection can prevent infections, combat antibiotic resistance and enable healing in infected burn wounds. The dressing becomes electrically active upon contact with bodily fluids.“Drug resistance in bacteria is a major threat, and antibiotic-resistant biofilm infections are estimated to account for at least 75 percent of bacterial infections in the United States,” said Chandan Sen, director of Ohio State’s Center for Regenerative Medicine & Cell Based Therapies, who led the study with colleagues at the Medical Center’s Comprehensive Wound Center and Center for Microbial Interface Technology. “This is the first pre-clinical long-term porcine study to recognize the potential of ‘electroceuticals’ as an effective platform technology to combat wound biofilm infection.”
Bacterial biofilms represent a major wound complication. Resistance of biofilm towards drug interventions calls for alternative strategies. Bacteria rely on electrostatic interactions to adhere to surfaces, an important aspect of biofilm formation. The concept that weak electric fields may have anti-biofilm property was first reported in 1992.
This study builds on Sen’s 2014 research with a wireless electroceutical dressing (WED) using silver and zinc printed on fabric. When moistened, WED generates a weak electric field without any external power supply and can be used like any other disposable dressing.
“The fact that wireless electric dressing is FDA-cleared and already in clinical use heightens the need to understand underlying mechanisms to enable optimal use,” Sen said. “Since it relies on electrical principles, it’s not subject to the mechanisms that may promote drug resistance. Understanding how this novel dressing may influence microbial, host and host-microbe interactions will determine the optimal use of this simple technology platform.”
During the study, WED dressing was applied within two hours of wound infection in pigs to test its ability to prevent biofilm formation. In addition, WED was applied after seven days of infection to study disruption of established biofilm. Wounds were treated with placebo dressing or WED twice a week for 56 days. Both proved successful, Sen said.
During burn injury, barrier function of the skin is breached, leaving the body vulnerable. Patients with burn injuries risk dehydration, along with the potential of foreign agents such as bacteria and allergen entering into the body and causing potential health complications.
 “Our study shows that WED may be viewed as a first generation electroceutical wound care dressing, and it also accelerated functional wound closure by restoring skin barrier function,” Sen said. “Both from bacterial biofilm structure as well as host response perspectives, WED was consistently effective. No batteries or wires are needed because we harness the power of electrochemistry."
“Our study shows that WED may be viewed as a first generation electroceutical wound care dressing, and it also accelerated functional wound closure by restoring skin barrier function,” Sen said. “Both from bacterial biofilm structure as well as host response perspectives, WED was consistently effective. No batteries or wires are needed because we harness the power of electrochemistry."
Ohio State researchers are teaming up with burn care team within the Department of Defense to start a clinical trial within the next month to test this technology on burn wounds in humans, Sen said.
Other Ohio State researchers involved in this study are Kasturi Ganesh Barki, Amitava Das, Sriteja Dixith, Piya Das Ghatak, Shomita Mathew-Steiner, Elizabeth Schwab, Savita Khanna, Daniel J. Wozniak and Sashwati Roy.
This research was partly supported by National Institutes of Health NR015676 and NR013898, along with these NIH awards: GM077185, GM069589, DK076566, AI097511 and NS42617.
Financial competing interest includes ownership of shares with Vomaris Innovations Inc. by Sen.
# # #
Media contact: Eileen Scahill, Wexner Medical Center Media Relations, 614-293-3737 or Eileen.Scahill@osumc.edu
