When you come to The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, you’ve taken the first step toward relief of your irritated skin. We’ll start by thoroughly listening to your needs, diagnosing what’s wrong and working closely with you to select a treatment plan to improve your life.
Those who are experiencing eczema or atopic dermatitis are provided the best care available, customized to your specific needs. For those experiencing eczema, our experts may suggest:
- Allergy skin testing to help diagnosis your condition
- Medicated creams to stop itching and repair your skin
- Medication to fight off an infection
- Advice for non-medication options, such as trying new soap or getting more sleep
If your needs are more advanced, our team can handle that as well. At Ohio State, you’ll have direct access to medical experts from across The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center -- Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute.
What are eczema and atopic dermatitis?
Eczema is an allergic condition that makes your skin dry and itchy, and it typically manifests in babies and children. It’s one of the most common chronic skin disorders and it isn’t contagious.
The most common type of eczema is atopic dermatitis. You can prevent many types of eczema by avoiding irritants, stress and the things you’re allergic to.
What causes eczema and atopic dermatitis?
Factors that can cause eczema include other diseases, irritating substances, allergies and your genetic makeup.
Common triggers for eczema include:
- Food allergies, including eggs, milk, wheat, corn and soy
- Environmental allergens, such as pollen, dust, animal dander and mold
- Skin irritants
- Lack of sleep and a quality diet
- Not enough sleep
People with atopic dermatitis often have asthma or seasonal allergies. There’s often a family history of allergies such as asthma, hay fever or eczema. While some people with atopic dermatitis test positive to allergy skin tests, atopic dermatitis is not caused by allergies.
What are the symptoms of eczema and atopic dermatitis?
The most typical symptoms of eczema are red, swollen and itchy skin. In a small child, the redness and itching are usually on the face and scalp. In school-age children or older, it’s more commonly found on the skin on the insides of the elbows and knees.
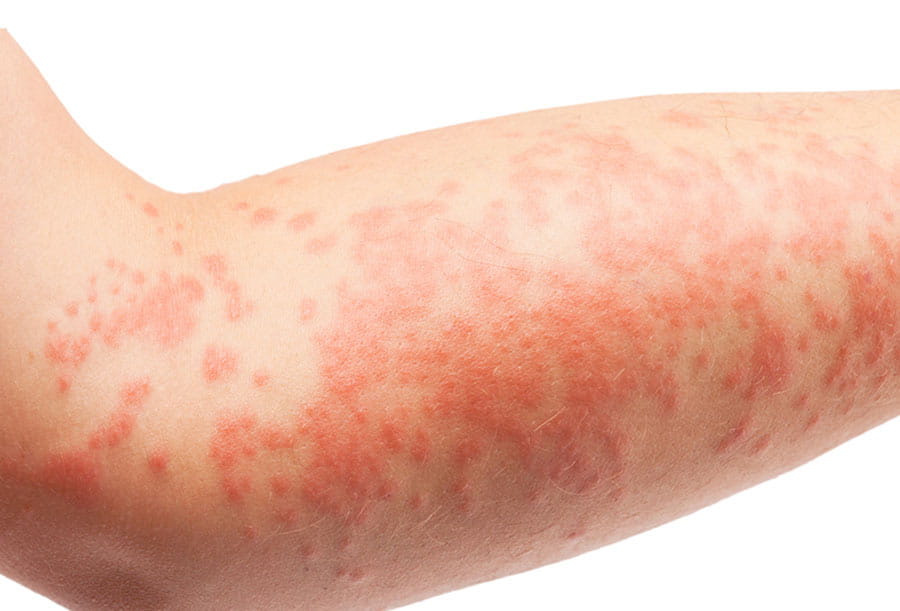 What does atopic dermatitis look like?
What does atopic dermatitis look like?
Atopic dermatitis can vary greatly from person to person. Many people will notice red to brownish-gray rashes, especially on the feet, ankles, hands, wrists, neck and upper chest.
What is the best eczema treatment?
A variety of treatment options exist for eczema. These are the most common:
Creams: Treatment options include medicated, or steroid, creams to control itching and repair damaged skin. These topical steroids can quickly decrease redness and itching, but long-term use carries risks of skin thinning and scarring.
Antibiotics: Your doctor may also prescribe an antibiotic medication. Bacterial staph infections of the skin are common in those who have atopic dermatitis.
Ultraviolet light: Ultraviolet light treatment is another promising new treatment, although this does come with an increased risk of skin cancer.
Preventing an outbreak is one of the best ways to manage your eczema. Our doctors suggest:
- Washing with non-soap cleansers
- Keeping your skin hydrated with a hypoallergenic moisturizer
- Protecting your skin from contact with household chemicals by wearing rubber gloves
Patient Forms
Additional Information
How would you like to schedule?
Don’t have MyChart? Create an account
